What is Blockchain Technology?
In today’s digital age, data security has become a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. With the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access to sensitive information, the need for robust and innovative solutions to protect data has never been more urgent. Enter blockchain technology—a revolutionary innovation that is transforming the way we secure and manage data. In this article, we’ll explore how blockchain technology enhances data security, its key benefits, and its potential applications across industries
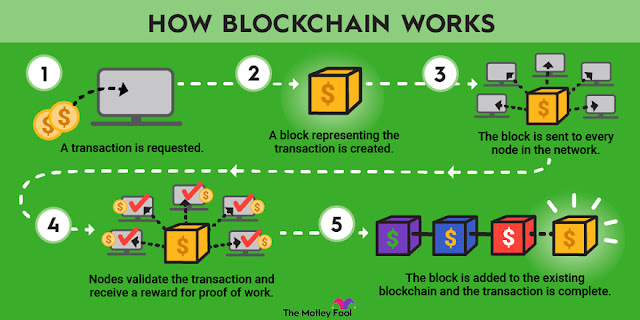
Blockchain is a decentralised, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional databases, which are centralized and controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where every participant (or node) has access to the same information. Each transaction is grouped into a "block" and linked to the previous one, forming a "chain" of blocks—hence the name "blockchain."
How Do Blockchains Operate?
A blockchain is made up of programs known as scripts that perform the same functions as a database, including entering and retrieving data as well as saving and keeping it in a location. Because a blockchain is distributed, several versions are stored on numerous computers, and for them to be legitimate, they must all match.
Transaction data is gathered by the Bitcoin blockchain and stored in a 4MB file known as a block (block sizes vary throughout blockchains). A cryptographic hash algorithm is applied to the block contents after it is full, producing a hexadecimal value known as the block header hash.
The term "blockchain" comes from the fact that the hash is then encrypted with the other data in the header of the subsequent block, forming a chain of blocks.
The key features of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, reducing the risk of manipulation or failure.
Transparency: All transactions are visible to participants in the network, ensuring accountability.
Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity.
Cryptography: Advanced encryption techniques secure data and protect it from unauthorized access.
How Blockchain Enhances Data Security
1. Decentralization Reduces Vulnerabilities
Traditional centralized systems are vulnerable to single points of failure. If a hacker gains access to the central server, they can compromise the entire system. Blockchain, on the other hand, distributes data across a network of nodes, making it nearly impossible for hackers to attack a single point. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network remains secure.
2. Immutable Records Ensure Data Integrity:
3. Advanced Cryptography Protects Data
4. Transparency and Accountability
5. Smart Contracts Automate Security
Applications of Blockchain in Data Security
Blockchain technology is being adopted across various industries to enhance data security. Here are some notable applications:
1. Financial Services
Blockchain is widely used in the financial sector to secure transactions, prevent fraud, and streamline processes. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on blockchain to ensure secure and transparent transactions.
2. Healthcare
3. Supply Chain Management
4. Identity Management
5. Voting Systems
The Future of Blockchain in Data Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for advanced data security solutions will only grow. Blockchain technology, with its unique combination of decentralisation, immutability, and cryptography, is poised to play a vital role in safeguarding data in the digital age. From securing financial transactions to protecting sensitive healthcare records, blockchain is revolutionizing the way we think about data security.
In the coming years, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of blockchain technology, as well as advancements that address its current limitations. By embracing blockchain, businesses and individuals can take a proactive approach to data security, ensuring that their information remains safe and secure in an increasingly interconnected world.
Key Takeaways
- The way that blockchains store information is different from that of regular databases; they store data in blocks that are connected by cryptography.Conclusion
- Although a blockchain can hold many kinds of data, transaction ledgers are the most popular application for it.
- Since the blockchain of Bitcoin is decentralised, all users collectively maintain control rather than any one individual or organisation.
- Data entered onto decentralised blockchains is irreversible since they are unchangeable. Transactions involving Bitcoin are permanently documented and publicly accessible.
Blockchain technology is more than just the foundation of cryptocurrencies—it’s a powerful tool for enhancing data security. Its decentralized nature, combined with advanced cryptographic techniques, makes it an ideal solution for protecting sensitive information in a wide range of industries. As we continue to navigate the challenges of the digital age, blockchain will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a more secure and trustworthy future.
By understanding the potential of blockchain and staying informed about its developments, we can harness its power to safeguard our data and build a more secure digital world.
The highest 6 Blockchain Companies:
1. Nu Holdings Ltd (NU)
- Revenue (TTM): $9.146 billion
- Revenue (2023): 8.029 billion
- Net income (TTM): $1.268 billion
- Market capitalization (Market Cap): $64.11 billion
- One-year trailing price return: 72.8%
- Exchange: NYSE
2. Coinbase Global, Inc. (COIN)
- Revenue (TTM): $3.973 billion
- Revenue (2023): $3.108 billion
- Net income (TTM): $1.349 million
- Market cap: $53.54 billion
- One-year trailing price return: 153.7%
- Exchange: Nasdaq
3 Core Scientific, Inc. (CORZ)
- Revenue (TTM): $561.04 million
- Revenue (2023): $502.4 million
- Net income (TTM): -$35.41 million
- Market cap: $1.80 billion
- One-year trailing price return: 153.7%
- Exchange: Nasdaq
4 MicroStrategy Inc. (MSTR)
- Revenue (TTM): $489.59 million
- Revenue (2023): $496.26 million
- Net income (TTM): -$85.19 million
- Market cap: $24.77 billion
- One-year trailing price return: 237.8% (as of Jul 15, 2024)
- Exchange: Nasdaq
5 Marathon Digital Holdings, Inc. (MARA)
- Revenue (TTM): $501.57 million
- Revenue (2023): $387.51 million
- Net income (TTM): $605.58 million
- Market cap: $5.67 billion
- One-year trailing price return: 23.19% (as of Jul 15, 2024)
- Exchange: Nasdaq
6 Riot Platforms, Inc. (RIOT)
- Revenue (TTM): $286.74 million
- Revenue (2023): $280.68 million
- Net income (TTM): $217.99 million
- Market cap: $2.83 billion
- One-year trailing price return: -44.5%
- Exchange: Nasdaq
Blockchain has finally achieved recognition, thanks in large part to Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, with numerous real-world uses for the technology already being investigated and put into practice. Blockchain, a buzzword that every investor in the world is using, has the potential to improve government and commercial operations by reducing the number of middlemen and increasing accuracy, efficiency, security, and cost.
As we enter the third decade of blockchain, the question of whether or whether legacy organisations will adopt the technology has been replaced with the question of when. These days, NFTs are widely used, and assets are being tokenised. Blockchains, tokens, and artificial intelligence might all be combined in business and consumer applications in the future.
Blockchain technology is more than just the foundation of cryptocurrencies—it’s a powerful tool for enhancing data security. Its decentralized nature, combined with advanced cryptographic techniques, makes it an ideal solution for protecting sensitive information in a wide range of industries. As we continue to navigate the challenges of the digital age, blockchain will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a more secure and trustworthy future.
By understanding the potential of blockchain and staying informed about its developments, we can harness its power to safeguard our data and build a more secure digital world.
FAQs
1. Is blockchain completely secure?
2. Can blockchain be hacked?
3. How does blockchain protect privacy?
4. What are the limitations of blockchain in data security?
Blockchain technology has some limitations, including scalability issues, high energy consumption (for proof-of-work blockchains), and the complexity of implementation. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges.



No comments:
Post a Comment